Drupal: the original modular open-source CMS
Drupal has recently been celebrating the 20th anniversary of its first release.
It was designed at the outset as a modular, open-source content management system. Its open-source specification means that the core is and has always been completely free of charge to developers, and the source code has been open for all to modify and improve upon. An active community of collaborative developers has also created numerous free add-on modules that may be downloaded and used by all Drupal developers.
Paid versions of some modules with advanced features such as e-commerce modules have also been made available by professional Drupal module developers. Licences to use these can be purchased or rented by either web development agencies or individual businesses running single websites.

Drupal version timeline
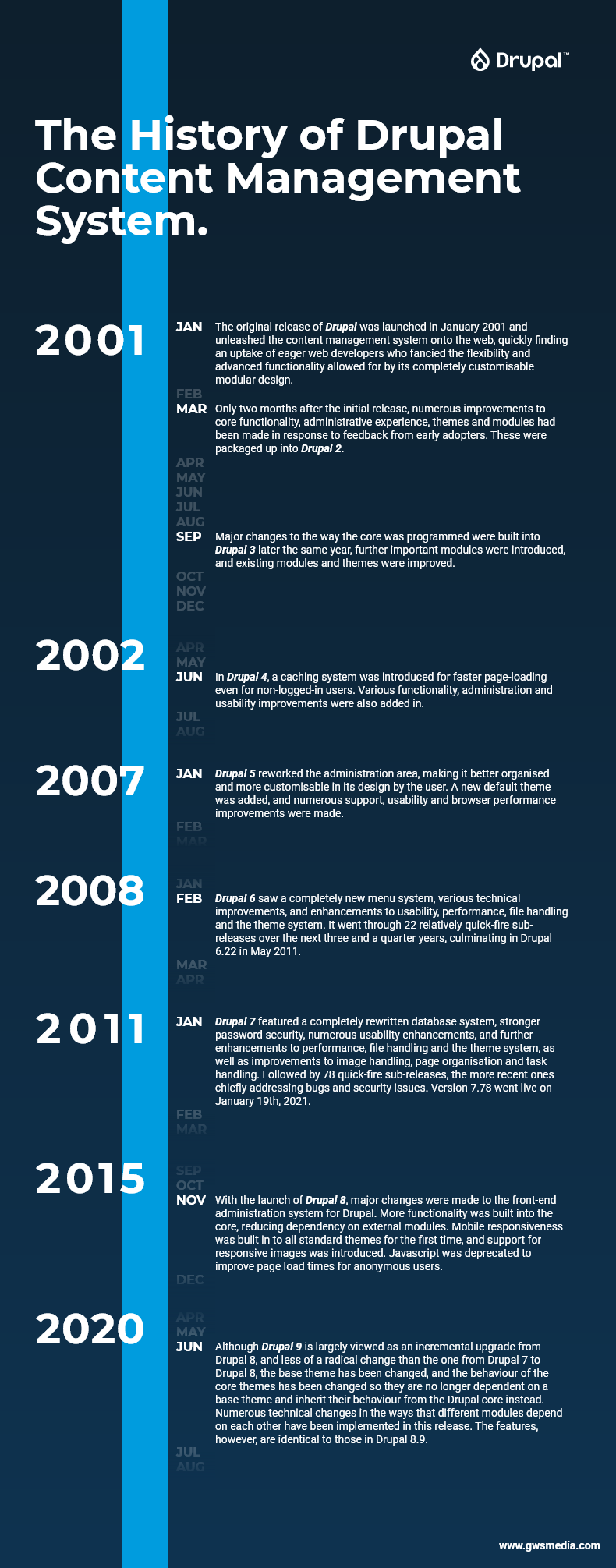
Drupal 1: January 2001
The original release of Drupal was launched in January 2001 and unleashed the content management system onto the web, quickly finding an uptake of eager web developers who fancied the flexibility and advanced functionality allowed for by its completely customisable modular design.
Drupal 2: March 2001
Only two months after the initial release, numerous improvements to core functionality, administrative experience, themes and modules had been made in response to feedback from early adopters. These were packaged up into Drupal 2.
Drupal 3: September 2001
Major changes to the way the core was programmed were built into the next major release later the same year, further important modules were introduced, and existing modules and themes were improved.
Drupal 4: June 2002
In the next major release, the following summer, a caching system was introduced for faster page-loading even for non-logged-in users. Various functionality, administration and usability improvements were also added in.
Drupal 4.1: February 2003
Although development continued at a fast rate after June 2002, it was decided to make the next significant updates sub-releases and not full releases. Thus, Drupal 4.1 was launched eight months after Drupal 4. This was followed at similar average intervals to the past intervals until version 4.7 was released in May 2006.
Each of these sub-releases introduced significant functionality or performance enhancements.
Drupal 5: January 2007
The next major release of Drupal reworked the administration area, making it better organised and more customisable in both design and layout. A new default theme was added, and numerous usability and browser performance improvements were made.
Drupal 6: February 2008
Only 13 months after the launch of Drupal 5, the decision was taken to call the update of February 2008 another major release – a timespan equivalent to the gap between 4.6 and 4.7.
Drupal 6 featured a completely new menu system, various technical improvements, and enhancements to usability, performance, file handling and the theme system.
At GWS, we started using Drupal with version 6, for clients including Mensa International.
Drupal 6 went through 22 relatively quick-fire sub-releases over the next three and a quarter years, culminating in Drupal 6.22 in May 2011 – four months after the initial release of Drupal 7.
Drupal 7: January 2011
Drupal 7 featured a completely rewritten database system, stronger password security, numerous usability enhancements, and further enhancements to performance, file handling and the theming system, as well as improvements to image handling, page organisation and task handling.
It was a very successful release and provided a combination of power, speed, security and long life which made it an attractive platform to develop with as well as providing an excellent solution for clients - for many years, it was the content management system we used at GWS for the majority of client websites.
It has been followed by 78 quick-fire sub-releases, the more recent ones chiefly addressing bugs and security issues. Version 7.79 was released live on April 7th, 2021.
Drupal 8: November 2015
With the launch of Drupal 8, major changes were made to the front-end administration system for Drupal. More functionality was built into the core, reducing dependency on external modules. Mobile responsiveness was built in to all standard themes for the first time, and support for responsive images was introduced. The media management system, configuration management system and content authoring and editing systems were overhauled. It was also very different 'under the hood' with Twig templates and the Symfony framework.
Drupal 8 changed the developer experience so much that many web developers as well as businesses whose websites were built in Drupal 7 were left with a dilemma of whether to keep using it or upgrade by rebuilding their sites in Drupal 8. Bearing in mind that it was a new system to learn and that there was no ready backwards compatibility or simple upgrade paths between the versions, many developers and web agencies moved away to alternative platforms as Drupal was becoming a more 'enterprise'-scale platform, and less appropriate for smaller or simpler websites.
Partly because of the challenges presented in upgrading from Drupal 7 to Drupal 8 for developers who were used to the older version and sites that relied on modules which were not available in Drupal 8, it was decided to extend support for Drupal 7 for more than ten years from its initial release, with its current scheduled end-of-life date being set for November 2022. Extended support may be available on a paid programme beyond then, until 2025, and it is likely that there may also be some long-term support projects.
Minor releases of Drupal 8 have since appeared approximately twice a year since April 2016.
Drupal 9: June 2020
In the same month as the release of Drupal 8.9, Drupal 9.0 was launched, offering a relatively straight-forward upgrade process for existing websites built in Drupal 8.8 and 8.9. Sites built in earlier versions of Drupal 8 have to be upgraded to at least 8.8 before a smooth upgrade to 9.0 is possible.
Drupal 9 imposes some more requirements on server performance and software versions than previous releases, requiring at least PHP version 7.3 and Apache 2.4.7 or above. APIs supported in Drupal 7 but deprecated in Drupal 8 have been eliminated from Drupal 9. As a result, many modules built for Drupal 7 that work in Drupal 8 will not work at all in Drupal 9 and require recoding from scratch, or replacement with newer alternatives providing equivalent functionality.
Although Drupal 9 is largely viewed as an incremental upgrade from Drupal 8, and less of a radical change than the one from Drupal 7 to Drupal 8, the base theme has been changed, and the behaviour of the core themes has been changed so they are no longer dependent on a base theme and inherit their behaviour from the Drupal core instead.
Numerous technical changes in the ways that different modules depend on each other have been implemented in this release. The features, however, are identical to those in Drupal 8.9.
Drupal 9.1: December 2020
The first significant sub-release to Drupal 9 appeared six months later, and introduced support for Composer 2 and PHP version 8, as well as lazy-loading for images with known dimensions, and improved installer performance. A new theme called Olivero that is planned to become the default Drupal theme at a later date was experimentally introduced.
Drupal 9.2: June 2021
Drupal 9.3: December 2021
Drupal 9.4: June 2022
Drupal 10: December 2022
Following releases of Drupal 9.2, 9.3 and 9.4, Drupal 10 was released in December 2022.
The new theme that was experimentally introduced for Drupal 9.1, Olivero, has replaced the existing Bartik design theme in Drupal 10. An updated, modern interface has replaced the outdated version, and offers even more ease for developers with WCAG compliance.
CKEditor 4 expires in 2023, so CKEditor 5 has been introduced to replace its long-standing predecessor (CKEditor 4 had been used for over 10 years). Along with being much more modern, this new version requires no separate installation as it is included in the Drupal 10 core.
Security-wise, Symfony 6 has superseded Symfony 4 to offer enhanced performance through the use of better bug and vulnerability fixes.
At the same time as the release of Drupal 10, a minor update to version 9, Drupal 9.5, was made available for those not yet ready to make a more major upgrade.
Benefits of Drupal for your Business or Organisational Website
Drupal allows you to have much broader and more complex control than Wordpress, without your developers having to write any extra code, since a lot can be done from within the admin system provided.
This means that various content types and entities can fairly easily be amended and added to, which is beneficial for both you as the client and for your website developers.
Drupal is more suited to websites that incorporate a lot of different types of content. A site with a simple pages and a news section would probably better off be done in Wordpress. But a site with pages, documents, news and a member area would be more suited to Drupal, owing to the complexity of each page type and how they all interact with each other.
More complex configurable permissions and access rights are also a good reason to use Drupal.
Drupal’s user interface takes some getting used to at first if you are accustomed to creating content in a Wordpress-based website, but with practice it is surprisingly easy to add and edit pages and other content and to edit the appearance and order of pages in the main navigation bar, although you might prefer to retain the services of a professional web agency to make changes you are unsure of or more complex additions and updates.
Summary
As we can see, Drupal has changed forms and developed its offering many times over the years but has not moved away from its original goal of being an open-source content management system enabling developers to continually progress and push the boundaries of what is possible for Drupal modules.
At GWS we have many years of experience working in Drupal and our developers are well versed in past features as well as staying on top of any new advancements. If you’re interested in a new website design or in upgrading an existing site, we’d be happy to advise on the best options and whether we think Drupal would be the best content management solution for your query. Explore our Content Management services here or get in touch with one of the team.